Alternatively, you can contact us like this:
Support Centre
Power Supplies A to Z : "V"
We've included this handy glossary to help with the terminology & abbreviations relating to power products. Pick a letter below to begin.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X-Z #V
Abbreviation for volt.
VA
Abbreviation for volt-ampere.
Vac
Acronym for volts of alternating current
Variable Resistor
See Potentiometer.
Varistor
Combination of Variable Resistor. A two-electrode semiconductor device having a non-linear, voltage-dependent resistance (usually a high resistance at low voltages and low resistance at high voltages). Often used to protect circuits against transient voltages.
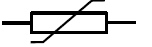
Schematic Symbol for a Varistor
Varnish Dip
The process of dipping a transformer or coil in varnish to bind or protect materials.
Vcc
Voltage Collector Collector. Positive supply voltage of a Bipolar Junction Transistor. The doubled suffix indicates that the voltage is common. i.e. it is the supply voltage to one (or more) collectors and not just the voltage at a specific collector.
Vdc
Acronym for volts of direct current
Vdd
Voltage Drain Drain. Positive supply voltage of a Field Effect Transistor. The doubled suffix indicates that the voltage is common. i.e. it is the supply voltage to one (or more) drains and not just the voltage at a specific drain.
VDE
Abbreviation for Verband Deutscher Elektrotechniker.
VDR
Abbreviation for Voltage Dependent Resistor.
Vee
Voltage Emitter Emitter. Negative supply voltage of a Bipolar Junction Transistor. The doubled suffix indicates that the voltage is common. i.e. it is the supply voltage to one (or more) emitters and not just the voltage at a specific emitter.
Verband Deutscher Elektrotechniker (VDE)
German organisation charged to test and to evaluate products, including power sources. See http://www.vde.com/vde_en/
Vias
See Plated Through Hole.
Volt (V)
Unit of measurement of electromotive force or potential difference. Symbol E, in electricity; symbol V in semiconductor circuits. A current of 1 A passing through a resistance of 1 ohm will produce a potential difference of 1 volt. See Ohm's Law. Written as 'volt'. Abbreviated to V.
Volt Microsecond / Volts per Microsecond
Rate of change of voltage over a period of time expressed in volts/microseconds.
Volt Second
In a control circuit, the on-time x the voltage applied to the winding is controlled (effectively running the magnetic component at peak magnetic flux density).
Volt Second Clamp
A circuit in the control of the pulse width modulator located in the primary which terminates the pulse when the volt seconds applied to the primary of the transformer exceeds a predetermined value.
Voltage
A derivative electrical quantity, E, measured in the units volts and defined in terms of the independently obtained ampere, I, and the unit or Resistance, ohm (R) by Ohm’s Law E=IR.
Voltage Balance
The difference in magnitude, in percent, between differential tracking output voltages of a power supply (PSU) where the voltages have equal nominal values with opposite polarities.
Voltage Clamp
See Clamp Circuit
Voltage Dependent Resistor
Another name for Varistor.
Voltage Divider
Tapped or series resistance or impedance across a source voltage to produce a lower output voltage.
Voltage Drop
Difference in potential between two points in a passive component or circuit.
Voltage Limit
Maximum or minimum value in a voltage range.
Voltage Limiting
Bounding circuit used to set specified maximum or minimum voltage levels.
Voltage Regulation
The process of holding voltage constant between selected parameters, the extent of which is expressed as a percent. See also Regulation.
Voltage Source
A power source that delivers constant voltage.
Voltage Stabilisation
The use of a circuit or device to hold an output voltage constant within given limits.
Volt-Ampere (VA)
Unit of Apparent Power.
Vss
Voltage Source Source. Negative supply voltage of a Field Effect Transistor. The doubled suffix indicates that the voltage is common. i.e. it is the supply voltage to one (or more) sources and not just the voltage at a specific source.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X-Z #

