Get in touch!
Alternatively, you can contact us like this:
If you're not sure which product you need, try our Quick Product Finder
Support Centre
Power Supplies A to Z : "R"
We've included this handy glossary to help with the terminology & abbreviations relating to power products. Pick a letter below to begin.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X-Z #R
Abbreviation for Resistance.
Radio Frequency Interference
An unwanted conducted or radiated signal. See also Electromagnetic Interference.
Rail
Either conductor of the output of a power supply. See Positive Rail, Negative Rail.
Rated Output Current
The maximum continuous load current a power supply (PSU) is designed to provide under specified operating conditions.
RC
Abbreviation for resistance-capacitance (usually referring to filters).
Reactance
In an ac circuit, reactance is the imaginary part of impedance. It is caused by the presence of inductors or capacitors in the circuit. Reactance is denoted by the symbol X and is measured in ohms ( Ω ).
Recovery Time
The time required for the measured characteristic to return to within specified limits following an abnormal event. See Overshoot.
Rectification
The process of changing an alternating current to a unidirectional current. See Full-Wave Rectifier, Half-Wave Rectifier.
Rectifier
A component that passes current only in one direction. E.g. a diode.
Redundancy
Use of multiple devices or modules to provide continued operation following most failures in a single module device.
Reference Ground
Defined point in a circuit or system from which potential measurements are made.
Reference Voltage
The defined or specified voltage to which other voltages are compared.
Regulated Power Supply
A device that maintains a constant output voltage or current within specified limits for specified changes in line, load, temperature or time.
Regulation
The process of holding selected parameters constant, the extent of which is expressed as a percent. Includes Voltage Regulation, Line Regulation, Load Regulation, Cross Regulation.
Regulator
The power supply (PSU) circuit that controls or stabilises the output parameter at a specified value.
Reinforced Insulation
Insulation with such mechanical and electrical qualities that it, in itself, provides the same degree of protection against electrical shock as double insulation. It may consist of one or more layers of insulating material. It is acceptable in place of double insulation. See Basic Insulation, Double Insulation, Supplementary Insulation.
Relay
A magnetic component or solid state device that opens or closes an isolated switch or switches when a voltage is applied to the control terminals.
Remanence
A measure of the remaining magnetization when the driving field is dropped to zero. See Hysteresis Loop, Coercivity.
Remote Enable/Inhibit
A logic signal applied to a power supply (PSU) to turn the unit on or off.
Remote Margining
See Margining.
Remote Programming
See Programming.
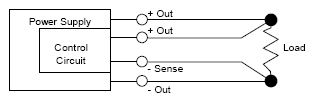
Remote sensing
Remote Sensing
A method to regulate the output voltage of a power supply (PSU) at the load by connecting the control circuit error-sensing leads directly to the load. Remote sensing compensates for specified maximum voltage drops in the load leads. Care should be taken to avoid opening load handling leads to avoid damaging the power supply (PSU). Polarity must be observed when connecting sense leads to avoid damaging the system. The sense leads carry very little current and steps should be taken to ensure that they do not pick up noise. They should either be screened or, if this is not possible, twisted together to minimise the noise pick up. Typically remote sensing is capable of adjusting for around 0.5V of drop in the connecting cables.
Required Headroom
The minimum voltage (above the required output voltage) supplied to a regulator, at which the regulator can provide the specified output.
Resistance (R)–
A measure of how much a component (or other object) opposes the flow of current. The unit of resistance is the ohm (Ω).
Resistor
A two terminal component with a defined resistance.
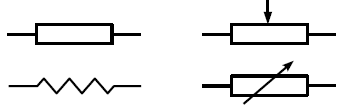
Schematic Symbols for a Resistor and Variable Resistor
Resonant Converter
A class of converters that uses a resonant circuit as part of the regulation loop.
Resonant Frequency
The natural frequency at which a circuit oscillates or a device vibrates. In an L-C circuit, inductive and capacitive reactances are equal at the resonant frequency.
Response Time
The time required for the output of a power supply (PSU) or circuit to reach a specified fraction of its new value after a step change or disturbance.
Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive (RoHS)
Often called the “lead-free” directive but it also covers maximum allowable concentration levels of 6 substances (Lead, Mercury, Cadmium, Chromium VI [Cr6+ or hexavalent chromium], PBB [polybrominated biphenyls] and PBDE [polybrominated diphenyl ether]). The maximum allowable concentration for Cadmium is 0.01% for the other 5 substances it is 0.1% by weight of homogeneous material. See also Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive.
Retentivity
See Remanence.
Return
The name for the common terminal of the output of a power supply (PSU), it carries the return current for the outputs.
Reverse Voltage Protection
A circuit or circuit element that protects a power supply (PSU) from damage caused by a voltage of reverse polarity applied at the input or output terminals.
RF
Abbreviation for Radio Frequency.
RFI
Abbreviation for Radio Frequency Interference.
Ripple
The periodic ac component at the power source output harmonically related to source or switching frequencies. Unless specified otherwise, it is expressed in peak-to-peak units over a specified bandwidth.
Ripple and Noise
See Period and Random Deviation (PARD).
Rise Time
The time required for a pulse to rise from 10% to 90% of its maximum amplitude.
rms Value
Abbreviation for Root Mean Square Value.
RoHS
Abbreviation of Restriction of Hazardous Substances (Directive).
Root Mean Square (RMS) Value
For a sine wave = √2 x Peak Value.
Rotary Encoder
An electronic component (usually used as a control input) which converts rotary motion into a series of electronic pulses. Used in the Z-UP and Z+ ranges of power supplies to enable intuitive user control of features of the power supply including voltage setting and current limit.
RS232
A standard for serial communications. Suitable for connecting one DTE (data terminal equipment [often a computer]) and one DCE (Data Communication Equipment [could be a power supply, or a modem, etc.]). See Communications Port.
RS485
A standard for serial communications. Suitable for connecting a controller to one or more pieces of equipment [such as a power supply]. Can be used to connect equipment over relatively large distances (1km). See Communications Port.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X-Z #

