Alternatively, you can contact us like this:
This form is protected by Cloudflare and their Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Support Centre
Power Supplies A to Z : "E"
We've included this handy glossary to help with the terminology & abbreviations relating to power products. Pick a letter below to begin.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X-Z #Earth
An electrical connection to the earth frequently using a grid or rod(s). See also Ground.
Earth Bond
See Bonding.
Earth Leakage Current
The ac or dc current to chassis/earth of a power supply (PSU) at a specified input voltage/frequency. Medical power supplies have specific requirements for Earth Leakage currents and this varies depending on standard to be met.
Effective Value
The value of a waveform that has the equivalent effect of a direct current. The Effective Value = RMS (Root Mean Square) Value
(For sine waves this equates to √2 x Peak value).
Efficiency
The ratio of total output power to total input power, expressed as a percentage, under specified conditions. Maximum theoretically possible efficiency is 100%. A power supply which is 90% efficient wastes one third as much power as a power supply which is 75% efficient. As efficiencies approach 100%, improvements become harder to achieve.
EIA
Abbreviation for Electronic Industries Association.
Eighth Brick
Industry standard footprint for dc-dc converters. Dimensions are 57.9mm x 22.8mm (2.3in x 0.9in). See also Full Brick, Half Brick, Quarter Brick, Sixteenth Brick. TDK-Lambda's PAE range of dc/dc converters are examples of eighth bricks.
Electricity
Property of matter that results from the presence or movement of electric charge.
Electrolytic Capacitor
A capacitor that contains two electrodes separated by an electrolyte.
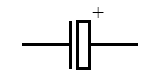
Schematic Symbol for an Electrolytic Capacitor
Electromagnet
A type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by a flow of electric current. The field disappears when the current stops.
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
The capability of equipment or systems to be used in their intended environment within designed efficiency levels without causing or receiving degradation due to unintentional EMI. EMC generally encompasses all of the electromagnetic disciplines.
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
Any electronic disturbance that does or could interrupt, obstruct, or otherwise impair the performance of electronic equipment. EMI is characterised by the following categories for test and measurement purposes: 1. Conducted Emissions, 2. Radiated Emissions, 3. Conducted Susceptibility, 4. Radiated Susceptibility.
Electromotive Force (EMF)
Force that causes free electrons to move in a conductor. Unit of measurement is the volt.
Electron (e-)
Negatively charged particle.
Electron Volt (eV)
A unit of energy. The energy acquired by an electron passing through a potential of one volt.
Electronic Industries Association (EIA)
US based trade group http://www.eia.org/
Electronic Load
Test equipment which draws controlled amounts of power or current from a power supply. Part of the ATE used to fully test a power supply during its functional testing stage.
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)
The flow of current that results when objects having a static charge come into a close enough proximity to discharge. Usually used to describe momentary unwanted currents that cause damage to electronic equipment / components.
Electrostatic Field
Electric field around a charged body.
Electrostatic Shield
A conductive screen that shunts induced energy to ground. See Faraday Shield.
EMC
Abbreviation for Electromagnetic Compatibility.
EMI
Abbreviation for Electromagnetic Interference.
EMI Filter
A circuit for the attenuation of the electromagnetic interference emitted from (or received by) a power supply (PSU) or other equipment. See also EMI.
EMV
Abbreviation for Elektromagnetische Verträglichkeit (German: Electromagnetic Compatibility).
EN
Abbreviation for Norme Européen (European Standard).
Enable
A signal input to a power supply which will turn on the outputs (if the unit is fan cooled then this may also enable the fan). The signal has to be activated to make the outputs turn on. With nothing connected to the input, the power supply should not operate. (Compare this with Inhibit).
Encoders
See Rotary Encoders
Energy
The capacity of a system to do work. The unit is joule.
Equivalent Series Inductance (ESL)
The amount of inductance in series with an ideal capacitor which exactly duplicates the performance of a real capacitor.
Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR)
The amount of resistance in series with an ideal capacitor which exactly duplicates the performance of a real capacitor.
ESD
Abbreviation for Electrostatic Discharge.
ESL
Abbreviation for Equivalent Series Inductance.
ESR
Abbreviation for Equivalent Series Resistance.
Ethernet
A serial communication bus mostly used to connect equipment in a LAN (local area network). Some power supplies can be supplied with Ethernet communications to allow remote control via the computer network. See Communications Port.
European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization
CENELEC is a non-profit technical organization set up under Belgian law and composed of the National Electrotechnical Committees of 30 European countries. In addition, 8 National Committees from neighbouring countries are participating in CENELEC work with an Affiliate status.CENELEC members have been working together in the interests of European harmonization since the 1950s, creating both standards requested by the market and harmonized standards in support of European legislation and which have helped to shape the European Internal Market. CENELEC works with 15,000 technical experts from 30 European countries. Its work directly increases market potential, encourages technological development and guarantees the safety and health of consumers and workers.
CENELEC’s mission is to prepare voluntary electrotechnical standards that help develop the Single European Market/European Economic Area for electrical and electronic goods and services removing barriers to trade, creating new markets and cutting compliance costs.
A Resolution of 7th May 1985 of the European Council formally endorsed the principle of reference to European standards within the relevant European regulatory work (Directives), thereby paving the way to a New Approach in the philosophy of regulations and standards in Europe. In the light of this New Approach, CENELEC is developing and achieving a coherent set of voluntary electrotechnical standards as a basis for the creation of the Single European Market/European Economic Area without internal frontiers for goods and services.
In addition to the traditional European standard deliverables, the dynamic Workshop (CWA: CENELEC Workshop Agreement) has been included in its portfolio, offering an open platform to foster the development of pre-standards for short lifetime products where time-to-market is critical.https://www.cencenelec.eu/
European Committee for Standardisation
(CEN) – (Comité Européen de Normalisation). Contributes to the objectives of the European Union and European Economic Area with voluntary technical standards which promote free trade, the safety of workers and consumers, interoperability of networks, environmental protection, exploitation of research and development programmes, and public procurement. https://www.cencenelec.eu/European Standard
standard adopted by CEN/CENELEC and carrying with it an obligation of implementation as an identical national standard and withdrawal of conflicting national standards.
Exa
SI prefix multiplier. Multiplies by 1018. So 100 EF = 100 x 1018 F. Written as 'exa'. Abbreviated to 'E'.
External Fusing
Criteria for externally fitted fuses in the input lines of a TDK-Lambda power supply.
Normally the internal fuse fitted in the power supply is rated approximately 20 - 25% greater than the maximum I/P current at low line and maximum load to overcome nuisance blowing.
The addition of external fusing is usually for one of the following reasons:
1. The supply is to be used in a medical application and therefore must have dual fusing.
2. To allow the customer to change fuses in the event of a problem because the unit fuse is NOT accessible. WARNING: If the fuse blows immediately after being replaced the Power Supply must be viewed as having a serious malfunction and must be returned to TDK-Lambda.
3. The Power Supply is to be connected to a non-polarised mains supply (where it is not certain which line is live).
It is important therefore, to consider the following when selecting fuses to be fitted externally to the Power Supply:
Any external fuse:
1. Should not be rated higher than the fuse fitted inside the power supply (the internal fuse rating is stated in the installation manual).
2. Should be a minimum of one rating below the fuse fitted in the Power Supply (see note 1)
3. Should have at least the same speed of response as the fuse fitted inside the power supply. e.g. FAST or SLOW acting.
4. Should have High Breaking Capacity.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X-Z #

