Alternatively, you can contact us like this:
This form is protected by Cloudflare and their Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Support Centre
Power Supplies A to Z : "T"
We've included this handy glossary to help with the terminology & abbreviations relating to power products. Pick a letter below to begin.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X-Z #t
Abbreviation for temperature (in °C).
Tank Circuit
TE
Unit of width (usually) in a 19 inch rack. 1 TE = 1 HP = 0.2 inches = 5.08mm.
Technischer Uberwachungs-Verein (TUV)
Laboratories licensed by the German government for testing electronic products to DIN, IEC and VDE standards. https://www.tuv.com/world/en/#Temperature Coefficient
The average percent change in output parameter (usually voltage) per degree Centigrade change in ambient temperature over a specified temperature range. (Expressed as %/°C). See also Ambient Temperature.
Temperature Derating
The amount by which power supply or component ratings are decreased to permit operating at elevated temperatures.
Temperature Effect
Temperature Range, Operating
See Operating Temperature Range.
Temperature Range, Storage
Tera
SI prefix multiplier. Multiplies by 1012. So 1 THz = 1 x 1012 Hz. Written as 'tera'. Abbreviated to 'T'.
Thermal Protection
Shuts down a power supply (PSU) if its internal temperature (or the temperature of specific components) exceeds a predetermined limit.
Thermal Runaway
A condition in a component where increasing temperature results in increasing losses bringing about a further temperature increase and so on. If left unprotected, this leads to failure.
Thermistor
A device which changes resistance with temperature. In power supplies, negative temperature coefficient thermistors frequently are used as inrush current limiting devices.
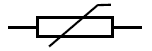
Schematic Symbol for a Thermistor
Three Terminal Regulator
A voltage regulator in a standard 3 terminal transistor package.
Three-Phase Electricity
Combination of three alternating currents having their voltages displaced by 120°, or 1/3 cycle. It is used for the distribution of high power electricity (all national electricity distribution networks distribute 3 phase electricity) and is particularly suited to high power loads.
Through Plated Hole
See Plated Through Hole.
Thyristor
A solid state device that has bistable electrical characteristics. Three common thyristor devices are diacs, Silicon-Controlled Rectifiers (SCR) and triacs.
Tolerance
Measured or specified percentage variation from nominal.
Top Hat Rail
See DIN Rail.
Topology
The arrangement of energy storage devices (inductors and capacitors) and power handling electronic switches and rectifiers which gives a switch mode power supply its operational capabilities. There are many topologies including Buck, Boost, Flyback, Sepic, 2-switch flyback, forward, 2-switch forward, active clamp forward, half-bridge, push pull, full bridge, phase shifted full bridge, soft switching 2-switch forward, resonant half bridge (modified LLC) (a patented topology used on TDK-Lambda's NV and EFE product ranges), etc. The correct topology to use is determined by the requirements of the power supply.
Toroid
A round magnetic core with a hole in the middle.
Total Regulation
The range of combined regulation tolerances such as the effects of input voltage variation, output load variation, temperature variation, drift and other specified variables. It is expressed as a plus/minus percent from nominal. Also called accuracy limit.
Tracking
A characteristic of a multiple-output power supply (PSU) that describes the changes in the voltage of one output with respect to changes in the voltage or load of another.
Tracking Over Voltage Protection (OVP)
A safety feature for power supplies with adjustable outputs where the trigger point of the OVP tracks with the voltage setting of the output such that a slow change in the output voltage will adjust the OVP setting but a fast change above the OVP point will trigger the OVP.
Transformer
Device which transfers energy from one circuit to another by electromagnetic induction. See Isolation Transformer, Step-Down Transformer, Step-Up Transformer.
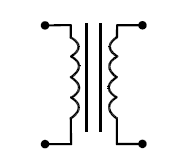
Schematic Symbol for a Transformer
Transient
A change in a given parameter, typically associated with input voltage or output loading.
Transient Effect
A short term effect on the steady state condition of a circuit.
Transient Recovery Time
The time required for the output voltage of a power supply (PSU) to settle within specified output accuracy limits following a transient. See Overshoot for drawing.
Transient Response
Response of a circuit to a sudden change in an input or output quantity. See Overshoot for drawing.
Transient Response Time
The time between introducing a transient (such as additional load) is introduced and the time the measured parameter (such as output voltage) returns and remains within a specified amplitude range. See Overshoot drawing.
Transistor
Solid state device which allows the current flow between two of its terminals depending on a smaller current (or voltage) applied to the third terminal. There are two main types of transistors, bipolar junction transistors and Field Effect Transistors.
Triac
A bi-directional silicon-controlled switch. It will conduct in both directions (from MT1 to MT2 or vice versa). See Silicon-Controlled Rectifiers (SCR)
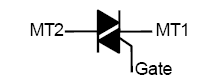
Schematic Symbol for a Triac
Trifilar
Three conductors wound side by side on a magnetic core or bobbin in which all three conductors are wound in the same operation.
True Power
Actual power generated or consumed in a circuit.
TTL
Abbreviation for transistor-transistor logic.
Tuned Circuit
Circuit containing capacitance, inductance and (optionally) resistance, connected in series or parallel, which when energised at a specific frequency known as its resonant frequency, an interchange of energy occurs between the coil and the capacitor.
Turns Ratio
The number of turns on the transformer primary winding divided by the number of turns on the secondary winding. A Step-Down Transformer has a turns ratio more than one while a Step-up Transformer has a turns ratio of less than one. Usually explicitly specified as input/output turns ratio.
TUV
Abbreviation for Technischer Uberwachungs-Verein
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X-Z #

