Alternatively, you can contact us like this:
This form is protected by Cloudflare and their Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Support Centre
Power Supplies A to Z : "L"
We've included this handy glossary to help with the terminology & abbreviations relating to power products. Pick a letter below to begin.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X-Z #L
The symbol for Inductance, and the abbreviation for litre and length.
Latch
A logic circuit that, once set, maintains the output at some fixed state until reset.
Latching Relay
A relay that mechanically latches until mechanically or electrically reset.
L-C Filter
A low pass filter consisting of an inductance (L) and a capacitance (C). Also known as an averaging filter.
Lead Resistance
Dc resistance of the leads of a circuit element or device.
Lead-Free Directive
See Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive.
Leakage Current
The ac or dc current flowing from input to output and/or chassis of an isolated device at a specified voltage. Also the off-state current in a switching device (diode, transistor, etc.) See also Earth Leakage Current.
LED
Abbreviation for Light-Emitting Diode.
Life Test
Estimating life expectancy of a device by subjecting it to accelerated or actual use.
Light-Emitting Diode (LED)
A semiconductor device which emits light when an electric current is passed through it. The colour is determined by the properties of the materials and dopants used.
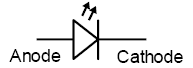
Schematic Symbol for LED
Line
The voltage across a power transmission line. See also High Line, Low Line.
Line Conditioner
A circuit or device designed to improve the quality of an ac line.
Line Effect
See Line Regulation.
Line Regulation
The amount that the output voltage changes as a result of changing the input voltage. Typically specified as a percentage change of the output for a given input voltage change with all other factors held constant. See also Regulation.
Line Transient
A perturbation outside the specified operating range of an input or supply voltage.
Linear
1) in a straight line.
2) quantities varying in direct proportion to one another.
Linear Power supply
See Linear Supply.
Linear Regulation
A regulation technique where the control device, such as a transistor, is placed in series (series regulation) or parallel (shunt regulation) with the load. The output is regulated by varying the resistance of the control device to dissipate unused power. See also Linear Supply.
Linear Regulator
A voltage regulator where a transistor (or Zener Diode, or other device) is used to control the output voltage. This method of regulation is inherently inefficient as the regulating device (transistor, etc.) is dropping volts at the full output current. Therefore wasted power = volts dropped x output current. For low current outputs, this wasted power is often not significant but for high current outputs, this wasted power can be very considerable and leads to the use of a Switched Mode Power Supply.
Linear Supply
An electronic power supply (PSU) employing Linear Regulation.
Litz Wire
Wire that consists of many thin, separately insulated wire strands woven together. It increases the surface area of the wire and reduces the skin effect and power losses when used in high-frequency applications.
Live
Electrically connected to a voltage source or electrically charged so as to have a voltage different from that of earth.
Load
Any combination of resistance, capacitance and inductance connected to the output of a power supply. It determines the requirements of the power supply (current, voltage, start up requirements, etc.).
Load Decoupling
Using filter components at the load to attenuate noise. See Decoupling.
Load Effect
See Load Regulation.
Load Impedance
The Impedance to the flow of current posed by the load.
Load Regulation
The percentage change in output voltage as the load is changed from a specified minimum to maximum (or maximum to minimum), with all other factors held constant. See also Regulation.
Load Transient Overshoot
See Overshoot.
Load Transient Response Time
Local Sensing
Using the power supply (PSU) output voltage terminals as the voltage sensing points to provide feedback to the voltage regulator. Benefit is only 2 wires connected to load, drawback is does not correct for voltage drop in the connecting leads. Compare with Remote Sensing.
Logic Enable/Inhibit
A referenced or isolated logic signal that turns a power supply (PSU) on or off.
Logic Ground
Common return or reference point for logic signals.
Logic High
A voltage representing a logic value of one (1) in positive logic. The absolute voltage level varies depending on the technology. For example, CMOS 3.7V is minimum for logic High, TTL = 2.0V.
Logic Low
A voltage representing a logic value of zero (0) in positive logic. The absolute voltage level varies depending on the technology. For example, CMOS 1.3V is maximum for logic low, TTL = 0.8V.
Long-Term Stability
The output voltage change of a power supply (PSU), in percent, due to time only, with all other factors held constant. Long-term stability is a function of component ageing (capacitors drying out, etc.).
Low Line
Lowest specified input operating voltage.
Low Voltage Directive (LVD)
Applies to all electrical equipment designed for use with a voltage rating of between 50 and 1000 V AC and between 75 and 1500 V DC. Broadly the scope of the LVD covers all products operating within those voltage limits with a few exceptions.
LVD
Abbreviation for Low Voltage Directive
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X-Z #

