Gerne können Sie uns auch telefonisch oder per E-Mail erreichen!
Support
Netzgeräte von A bis Z : "G"
Wir haben dieses praktische Glossar aufgenommen, um Sie bei Terminologie und Abkürzungen in Bezug auf Stromprodukte zu unterstützen. Wählen Sie einen der folgenden Buchstaben aus.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X-Z #Galvanic
Related to direct-current electricity or dc.
Galvanic Isolation
Separation of the signal/power source (or sink) in such a way that dc current cannot bridge the connection. There are two generally accepted methods for galvanic isolation: use of transformers or use of optical isolators. Both allow the ac component of a signal to pass, but not the dc component.
General Purpose Interface Bus
A parallel communications bus. Used to connect electronic test and measurement devices to control equipment (such as a computer). Also known as IEEE488. See Communications Port.
Giga
SI prefix multiplier. Multiplies by 109. So 100 GHz = 100 x 109 Hz. Written as 'giga'. Abbreviated to 'G'.
Glitch
An unwanted transient voltage spike occurring on a signal.
GPIB
Abbreviation of General Purpose Interface Bus.
Ground
A conducting connection, whether intentional or accidental, by which an electric circuit or equipment is connected to earth, or to some conducting body that serves in place of earth.
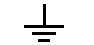
Schematic Symbol for Ground (or Earth)
Ground Bus
A bus, grounded in at least one place, to which individual grounds in a system are attached.
Ground Grid
Interconnected bare conductor arranged in a pattern over a specified area, laid out on or below the earth’s surface.
Ground Loop
A condition that occurs when there is more than one ground connection path between two pieces of equipment or circuits. These multiple paths produce a similar effect to a loop antenna which will pick up and radiate interference.
Ground Plane
1) A layer of copper on a PCB providing a low impedance ground return to all circuit elements needing it. Also for shielding.
2) A conductive surface serving as the circuit reference ground or as a near-field reflection point for an antenna.
Ground Rod
A metal rod, usually copper clad, driven into the earth to serve as a ground terminal.
Grounded
Connected to a common reference point (usually earth).
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X-Z #

